OLAP is a widely spread technology belonging to Business Intelligence processes developed to coordinate and analyze vast amounts of data. OLAP databases are stored in the form of multidimensional cubes where each cube comprises the data supposed relevant by a cube administrator. Through certain OLAP operations, a user is able to obtain a specified view of the cube and extract requisite information from it. So this way it’s possible to get a necessary Pivot Table and Pivot Chart report.
General OLAP operations involve Drill-up, Drill-down, Pivot, and Slice-and-Dice. Here we’d like to expand the list and look through all possible OLAP operations with examples for data mining including slicing and dicing in OLAP.
But before defining what is OLAP operation, let’s figure out what language is used in this process.
OLAP language
OLAP operations could be based on two OLAP languages: SQL and MDX.
SQL or Structured Query Language is a computer language developed to work in two dimensions in order to manage relational database and manipulate data.
MDX or Multidimensional expressions is a language for analytical queries expression. Its principle difference from SQL language is that MDX is able to reference multiple dimensions. Microsoft primarily invented MDX as a SQL extension.
These two languages are different and have their own peculiarities. However, OLAP operations using SQL and MDX languages are pretty similar.
Our product Ranet OLAP uses MDX query language, that is why today we made an accent on MDX OLAP operations example.
OLAP operations:
So let’s outline the typical OLAP operations now.
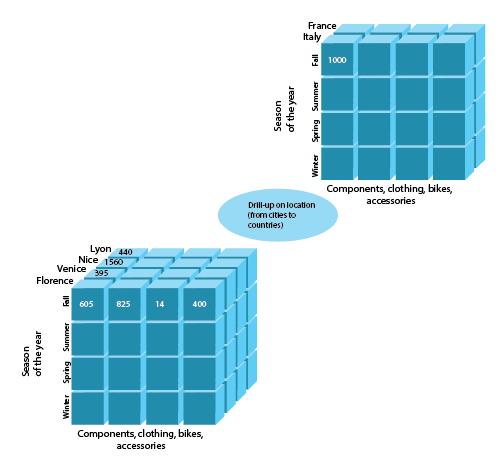
Drill Up
This operation you can meet as a part of pair drill up and drill down in OLAP. Drill-up is an operation to gather data from the cube either by ascending a concept hierarchy for a dimension or by dimension reduction in order to receive measures at a less detailed granularity. So that to see a broader perspective in compliance with the concept hierarchy a user has to group columns and unite the values. As there are fewer specifics, one or more dimensions from the data cube will be deleted, when this OLAP operation is run. In some sources drill up and roll up operations in OLAP come as synonyms, so this variant is also possible.
Here’s a typical example of a Drill-up or roll up OLAP operations example:
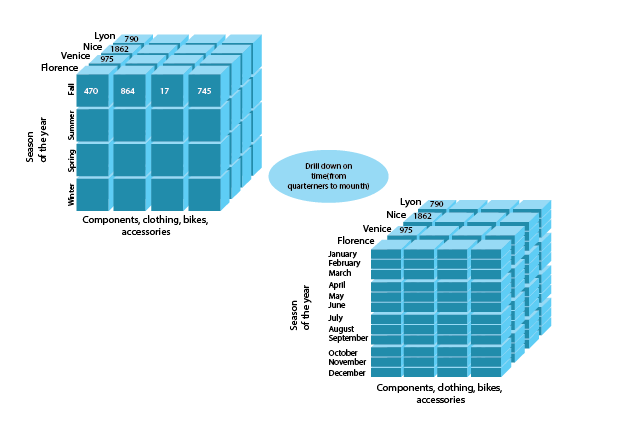
Drill down
OLAP Drill-down is an operation opposite to Drill-up. It is carried out either by descending a concept hierarchy for a dimension or by adding a new dimension. It lets a user deploy highly detailed data from a less detailed cube. Consequently, when the operation is run, one or more dimensions from the data cube must be appended to provide more information elements.
Have a look at an OLAP Drill-down example in use:
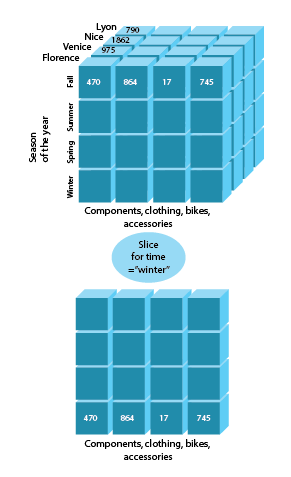
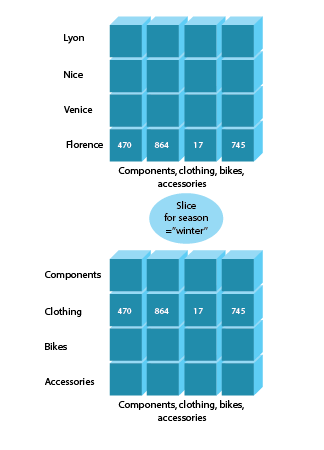
Slice
The next pair we are going to discuss is slice and dice operations in OLAP. The Slice OLAP operations takes one specific dimension from a cube given and represents a new sub-cube, which provides information from another point of view.It can create a new sub-cube by choosing one or more dimensions. The use of Slice implies the specified granularity level of the dimension.
OLAP Slice example will look the following way:
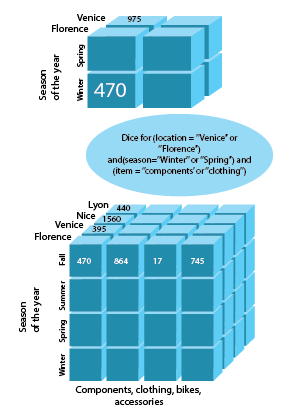
Dice
OLAP Dice emphasizes two or more dimensions from a cube given and suggests a new sub-cube, as well as Slice operation does. In order to locate a single value for a cube, it includes adding values for each dimension.
The diagram below shows how Dice operation works:
Pivot
This OLAP operation rotates the axes of a cube to provide an alternative view of the data cube. Pivot clusters the data with other dimensions which helps analyze the performance of a company or enterprise.
Here’s an example of Pivot in operation:
Scoping
The operation of Scoping restrains the presentation of the database objects to a specified subset. It will let users receive and update certain data values which they want. If there is a huge amount of data and a user needs to constrain the access of information to a specified subset Scoping is mostly conducive.
Screening
Screening is conducted to limit the set of data extracted.
Drill across
Drill across and Drill through in OLAP are another pair of opposite operations. The operation Drill across reconciles cells from several data cubes which share the same scheme.
Drill through
OLAP Drill through enables to navigate from data at the lower level in a cube to data in the operational systems whence the cube was ejected. The operation is usually exploited to identify the cause of outlier values in a data cube.
Sort
Sort brings the cube back where the members of a dimension were sorted.
Add Measure
Thanks to this OLAP operation one is able to add new measures to a cube.
Drop Measure
In contrast to Add Measure, it’s also possible to get rid of a measure from a data cube if it's not necessary.
Union
Due to an opportunity of Union, you can unite a number of cubes which have the same scheme but separate instances.
Difference
Difference eliminates the cells in a cube which are owned by another one. These two cubes must possess the same scheme.
Questions
In order to summarize everything up, let’s go through the top asked questions about OLAP operations.
- How to define the concept of OLAP and the operations it supports?
Online Analytical Processing is a technology, which helps to perform business data multidimensional analysis and operate complex calculations and data modeling. OLAP databases are stored in the form of multidimensional cubes where each cube comprises the data supposed relevant by a cube administrator. OLAP operations aimed to help user to obtain a specified view of the cube and extract requisite information from it.
- What are different types of OLAP operations?
We can distinguish 14 basic OLAP operations:
- Drill-up
- Drill-down
- Slice
- Dice
- Pivot
- Scoping
- Screening
- Drill across
- Drill through
- Sort
- Add measure
- Drop measure
- Union
- Difference
More info you can find in the beginning of the article where we discussed the typical OLAP operations with examples.
- What is difference between slice and dice in OLAP?
The Slice operation takes one specific dimension from a cube given and represents a new sub-cube which provides information from another point of view. The Dice operation in the contrary emphasizes two or more dimensions from a cube.
In conclusion, its a must to point out that OLAP system contains all historical processing of information which you’ll be able to see in a summarized and multidimensional view drawing on the operations described above. Through them, the data will turn out flexible and user-friendly to analyze.